EU solar generation increased by over 20% for the fourth year running in 2025, with its share in the energy mix surpassing coal and hydro. For the first time in history, solar and wind generated more energy in the EU than fossil fuels.
Solar generated a record 369 TWh of energy across the EU in 2025, according to the European Electricity Review published by energy think tank Ember.
The result is an increase of 62 TWh on 2024 and more than doubles the 145 TWh generated in 2020. Ember says solar energy has grown at an average annual growth in generation of 21% over the past five years, a rate far beyond any other energy source.
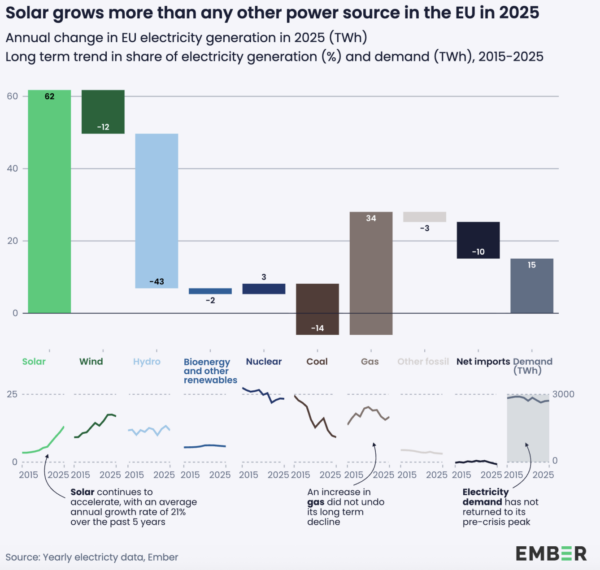
This growth trajectory, buoyed by an added 65.1 GW of solar in the EU last year, led solar to generate a record 13% of the bloc’s power in 2025, moving ahead of coal and hydro. Every EU country saw growth in solar generation increase year-on-year last year, led by Hungary with a 28% contribution to its power mix. In Cyprus, Greece, Spain and the Netherlands, solar’s share in the electricity mix was also over 20%.
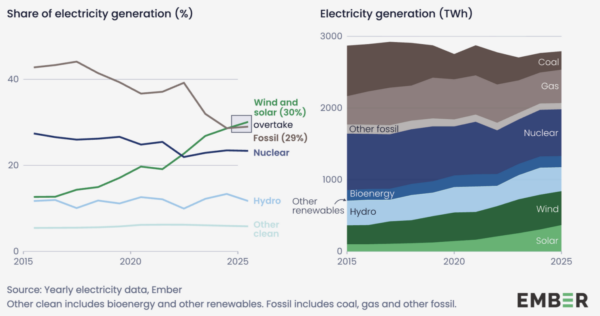
For the first time in history, solar and wind energy generated more EU electricity than fossil fuels in 2025, together responsible for a record 30% of EU power ahead of fossil fuels’ 29%. Solar and wind generated more electricity than all fossil sources in 14 of the EU’s 27 member states.
Report author Beatrice Petrovich said the milestone shows just how rapidly the EU is moving towards a power system backed by wind and solar. “As fossil fuel dependencies feed instability on the global stage, the stakes of transitioning to clean energy are clearer than ever,” Petrovich said.
In 2025, 19 EU countries recorded at least one hour when wind and solar combined accounted for over 70% of the country’s hourly power generation, compared to only two countries in 2020. Ember found wind and solar supplied more than half of electricity generation during at least one third of all hours in Denmark, Estonia, Germany, Greece, Lithuania, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal and Spain.
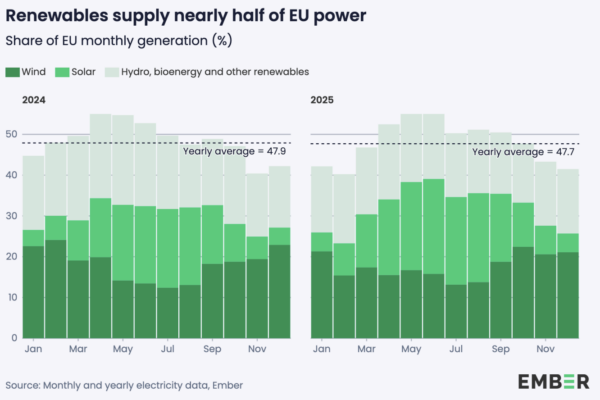
Ember’s report adds that all renewable sources, comprising solar, wind, hydro, bioenergy and other renewables, generated a total 1,331 TWh of energy in the EU last year for a 47.7% share of the total mix, 0.2% down on the year prior. The report says the share remained stable as the weather conditions that caused a drop in wind and hydro output boosted solar generation.
While gas generation rose by 8% compared to 2024, pushing the EU power sector’s gas import bill up to €32 billion, coal power fell to a historic low of 9.2%, with 19 EU countries now generating less than 5% of their energy from coal.
As solar and wind energy becomes the backbone of Europe’s power system, Ember’s report says electricity storage, together with grid enhancements and demand flexibility, will be crucial to put increasingly abundant renewable power to use and displace imported fossil power.
Among a series of recommendations listed in the report is removing barriers to battery deployment in national legislation, EU member states collaboration on permitting for key cross-border power lines, supporting investment in heat pumps and other electric technologies, introducing policy for electrifying transport, heating, and industry via the forthcoming Electrification Action Plan and delivering legislation to ban Russian gap and LNG imports by 2027.
via pv magazine International https://ift.tt/UmZyFY6
Categories: Energy
